As the backbone of modern business operations, an office network connects employees, devices, and resources, enabling efficient communication and data sharing. However, with increased connectivity comes heightened security risks. Cyberattacks can compromise sensitive data, disrupt workflows, and damage reputations.
A firewall is one of the most critical tools for protecting an office network. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of firewalls, their importance, and steps to secure your office network effectively.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall acts as a security barrier between your office network and the internet, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules. Think of it as a gatekeeper that ensures only authorized traffic passes through while blocking potentially harmful data packets.
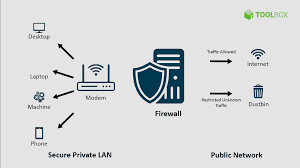
How Does a Firewall Work?
Firewalls operate by applying predefined security rules to analyze data packets. They can perform tasks like:
- Allowing traffic from trusted sources.
- Blocking traffic from suspicious or unknown sources.
- Logging network activity for future review.
Types of Firewalls
- Hardware Firewalls
- Physical devices installed between your network and the internet.
- Best for protecting an entire office network.
- Software Firewalls
- Applications installed on individual devices.
- Offer protection at the device level.
- Cloud-Based Firewalls
- Hosted in the cloud, ideal for businesses with remote workers.
- Scalable and easy to manage.
Why Do You Need a Firewall for Your Office Security?
- Prevents Unauthorized Access: A firewall blocks unauthorized users or hackers from accessing your network, protecting sensitive data.
- Protects Against Malware and Viruses: Firewalls can detect and block malicious traffic, preventing malware, ransomware, and viruses from infiltrating your systems.
- Enhances Network Performance: By filtering unnecessary traffic, firewalls improve network efficiency, ensuring critical business processes run smoothly.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries require businesses to implement firewalls as part of data security regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Essential Firewall Features for Office Networks
When choosing a firewall for your office, look for these key features:
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS): Monitors network traffic for suspicious activities and takes action to prevent potential threats.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Support: Allows secure remote access for employees working from home or traveling.
- Content Filtering: Blocks access to non-business-related or harmful websites, enhancing productivity and security.
- Advanced Threat Protection (ATP): Detects and mitigates sophisticated threats like zero-day exploits.
- Scalability: Ensure the firewall can accommodate your growing office needs.
Steps to Secure Your Office Network Using Firewalls
Step 1: Assess Your Office Network
- Identify all devices connected to your network, including computers, servers, printers, and IoT devices.
- Map out your network architecture to understand data flow and potential vulnerabilities.
Step 2: Choose the Right Firewall
- For Small Offices
- Consider all-in-one devices like the SonicWall TZ series or Cisco Meraki MX64 for ease of use and affordability.
- For Medium to Large Offices
-
- Opt for enterprise-grade solutions like the Fortinet FortiGate or Palo Alto Networks PA Series for advanced features and scalability.
- For Remote or Hybrid Workforces
- Choose cloud-based firewalls like Zscaler or Barracuda CloudGen Firewall for seamless remote access.
Step 3: Configure Firewall Settings
- Set up security policies to allow only necessary traffic.
- Enable intrusion detection systems and automatic updates to keep the firewall software current.
- Use a default deny rule to block all traffic by default and allow specific traffic as needed.
Step 4: Segment Your Network
- Divide your network into smaller segments using Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs).
- For example, separate employee workstations, servers, and guest Wi-Fi networks to limit potential damage if one segment is compromised.
Step 5: Monitor and Update Regularly
- Use the firewall’s monitoring tools to analyze traffic patterns and detect anomalies.
- Schedule routine updates to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security features.
Step 6: Train Employees
- Educate employees about the importance of network security and safe browsing practices.
- Regularly remind staff to avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unverified files.
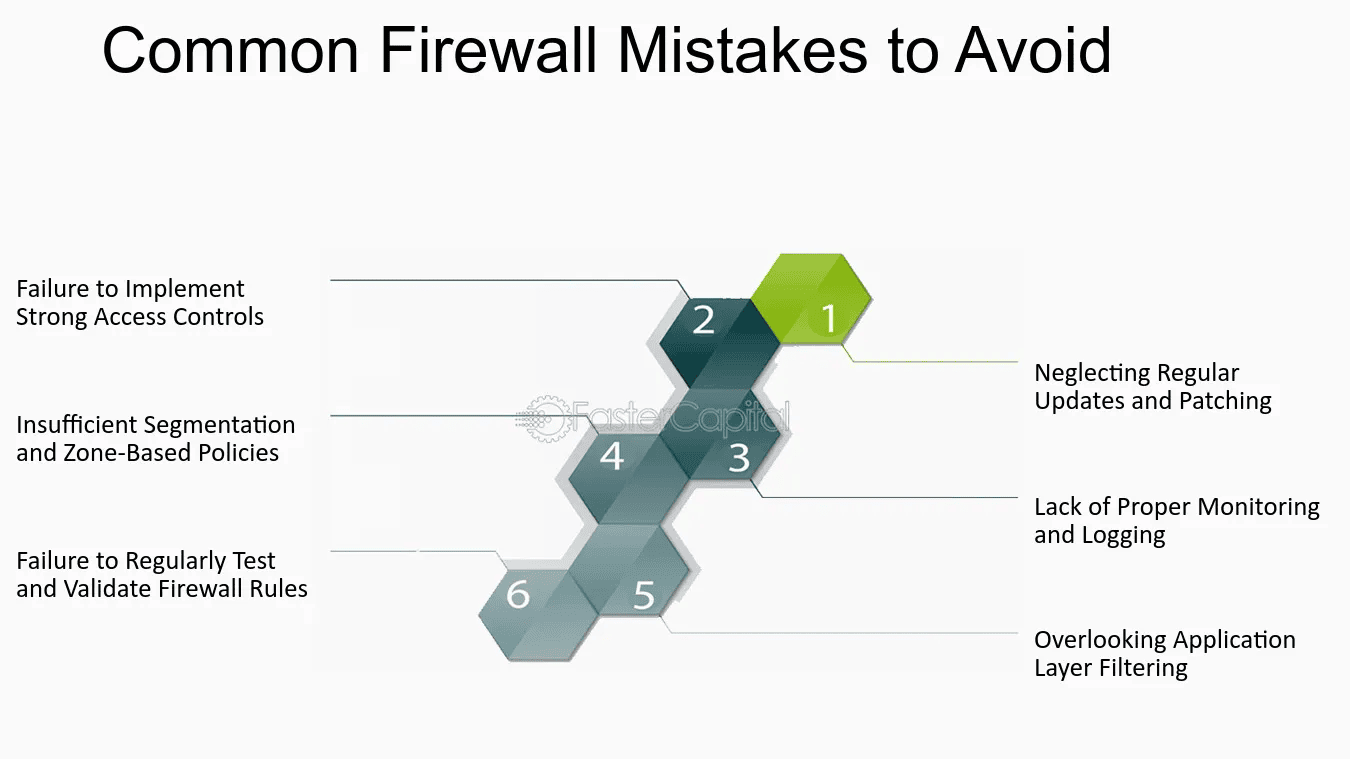
Common Firewall Mistakes to Avoid
- Neglecting Regular Updates: Outdated firewalls are more susceptible to new threats.
- Using Default Settings: Default passwords and configurations are easy targets for hackers.
- Overcomplicating Rules: Too many rules can cause performance issues and make it harder to manage the firewall.
- Ignoring Outbound Traffic: While most focus on incoming threats, monitoring outgoing traffic is equally important to prevent data exfiltration.
Complementing Firewalls with Additional Security Measures
A firewall alone cannot guarantee complete security. Pair it with these tools for a robust defense:
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Protect individual devices from malicious files and programs.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security to logins, making it harder for attackers to breach accounts.
- Regular Backups: Ensure critical data is backed up securely to minimize downtime during an attack.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Integrates firewall logs with other security tools for a comprehensive overview of network activity.
Cost of Implementing a Firewall
Hardware Firewalls
- Small offices: $300–$1,000
- Large enterprises: $1,000–$10,000+
Software Firewalls
- Starting at $50 per device annually.
Cloud-Based Firewalls
- Subscription-based pricing, typically $10–$50 per user per month.
Best Practices for Maintaining a Secure Office Network
- Perform Regular Security Audits: Identify and fix vulnerabilities.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles.
- Use Strong Passwords: Enforce password policies to ensure secure logins.
- Enable Automatic Backups: Minimize downtime and data loss during attacks.

Conclusion
Firewalls are a cornerstone of office network security, acting as the first line of defense against cyber threats. By understanding your network’s needs and configuring the right firewall solution, you can significantly enhance your office’s data security. While firewalls are crucial, they work best as part of a comprehensive security strategy that includes antivirus software, encryption, and employee training. Furthermore, investing time and resources into securing your office network today can save you from costly breaches and downtime tomorrow.








Leave a comment