Data centers are facilities that house critical IT infrastructure for organizations, including servers, storage, networking equipment, and other computing resources. For a data center to operate efficiently, specific infrastructure components are necessary to support power, cooling, and organization of IT equipment. This article explores three fundamental components of data center infrastructure: cooling systems, server racks and cabinets, and power distribution units (PDUs).
Cooling Systems
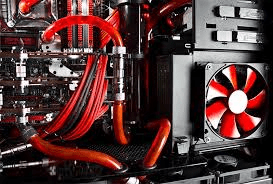
Cooling is one of the most essential aspects of data center infrastructure. Servers and other IT equipment generate significant heat, and without effective cooling, they can overheat, leading to potential malfunctions, downtime, and reduced equipment lifespan. Two common cooling methods used in data centers are air cooling and liquid cooling.
Air Cooling
Air cooling is the traditional and most widely used cooling method in data centers. It involves moving cool air through server racks to lower the temperature of equipment.
Key Components of Air Cooling Systems:
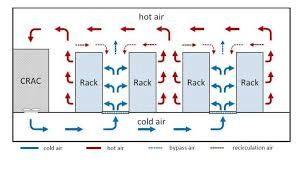
- CRAC (Computer Room Air Conditioning) Units: CRAC units cool the air and circulate it within the data center. They function similarly to commercial air conditioners but are optimized for continuous operation.
- Cold Aisles and Hot Aisles: To improve airflow efficiency, data centers often use hot and cold aisle configurations. Servers are aligned so that their intake (cold air) faces one aisle and their exhaust (hot air) faces the other. Raised Floors and Overhead Ducts: Raised floors allow cool air from CRAC units to move under the floor and be directed into the cold aisles, while overhead ducts can channel hot air away from equipment.
Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling, though less common than air cooling, is becoming popular in high-performance computing environments that generate excessive heat. Liquid has a higher heat capacity than air, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation.
Types of Liquid Cooling Systems:
- Direct-to-Chip Cooling: This method involves placing a cooling plate on each server’s CPU and GPU. A liquid coolant flows through the plate, absorbing heat and transporting it out of the server.
- Immersion Cooling: In immersion cooling, servers are submerged in a non-conductive liquid that absorbs and dissipates heat. This method is highly efficient but requires specialized equipment and setup.
- Chilled Water Systems: Chilled water circulates through pipes connected to cooling coils inside CRAC units. The water absorbs heat and is then pumped back to the chiller to cool down, making it ready for another cycle.
Choosing Between Air and Liquid Cooling
Air cooling is typically more cost-effective and easier to implement in traditional data centers, while liquid cooling is ideal for environments with high-density or high-performance computing needs where air cooling might not be sufficient.
Server Racks and Cabinets
Server racks and cabinets are essential for organizing IT equipment within a data center. They provide a structure to mount servers and other networking hardware, optimize space, and ensure efficient airflow.
Types of Server Racks and Cabinets
- Open Frame Racks: Open frame racks lack side panels and doors, making them ideal for maximum airflow and easy access to equipment. They are typically used in secure data centers with controlled environments.
- Enclosed Cabinets: These cabinets are fully enclosed, with side panels, doors, and often locks for security. They protect equipment from dust and physical damage and are common in multi-tenant data centers where additional security is necessary.
- Wall-Mount Racks: These compact racks are mounted on walls and are used in smaller facilities or remote offices. They are suitable for limited equipment and offer a space-saving option.
- Rack Units (U): The height of racks is measured in units (U), with each U equal to 1.75 inches. Common rack sizes range from 24U to 48U, with larger racks supporting more equipment.
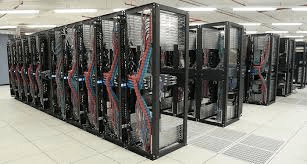
Importance of Proper Rack Management
Efficient rack management promotes airflow, simplifies cable organization, and enhances security. Many data centers use cable management accessories, such as horizontal and vertical cable managers, to prevent cables from obstructing airflow.
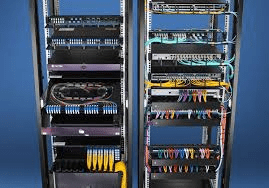
Rack Cooling and Ventilation
Proper airflow within server racks is vital for keeping servers cool. This is often achieved through:
- Perforated Doors: Enclosed cabinets with perforated doors allow for better airflow.
- Rack-Mounted Cooling Units: For high-density setups, rack-mounted cooling units can provide additional cooling directly to equipment within a rack.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
- PDUs are devices that distribute power from a primary source (such as an uninterruptible power supply) to multiple outlets within the server racks. They are essential for providing stable, uninterrupted power to servers and networking equipment.
Types of PDUs
- Basic PDUs: These PDUs simply distribute power without advanced features. They are generally used in small or low-density data centers where power monitoring is unnecessary.
- Metered PDUs: Metered PDUs allow data center operators to monitor power consumption at the PDU level. They provide valuable insights into energy usage, helping optimize power distribution.
- Monitored PDUs: These PDUs offer remote monitoring capabilities, allowing IT administrators to track power usage in real-time and receive alerts for potential issues.
- Switched PDUs: Switched PDUs enable administrators to control individual outlets remotely, allowing them to turn specific equipment on or off as needed. This feature is helpful for power cycling and troubleshooting.

Choosing the Right PDU for Your Data Center
The selection of PDUs depends on the data center’s power requirements, equipment density, and monitoring needs. Switched and monitored PDUs are often used in larger data centers, while basic PDUs may suffice for smaller setups with limited equipment.
Importance of Redundancy in Power Distribution
To prevent power-related failures, many data centers implement redundancy at the PDU level. This involves using dual power supplies for critical equipment and connecting each supply to separate PDUs. This setup ensures that equipment remains operational even if one PDU fails.
Optimizing Data Center Infrastructure for Efficiency
The right combination of cooling systems, server racks, cabinets, and PDUs can significantly impact a data center’s operational efficiency and reliability. Here are some best practices to enhance infrastructure:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure that all components, especially cooling systems and PDUs, are regularly maintained to avoid performance degradation.
- Environmental Monitoring: Use temperature and humidity sensors to monitor environmental conditions and adjust cooling as necessary.
- Cable Management: Organized cabling reduces airflow blockage and facilitates easier equipment access during maintenance.
Conclusion
Data center infrastructure forms the foundation of an efficient and reliable data center. Cooling systems prevent equipment from overheating, server racks and cabinets organize and secure hardware, and PDUs provide stable and reliable power distribution. By investing in quality infrastructure components and following best practices, organizations can create data centers that support high performance, scalability, and uptime.
The strategic selection of these components contributes to an environment where servers and networking equipment can operate optimally, ensuring data integrity and consistent service availability.
By following these guidelines and using the accompanying images as visual aids, data center managers can make informed decisions on infrastructure design, ultimately resulting in more reliable and efficient facilities








Leave a comment