Data is the lifeblood of modern businesses, and its safety and availability are critical. A robust backup strategy ensures that organizations can recover from accidental deletions, hardware failures, or cyberattacks. Backup solutions encompass various tools and technologies tailored to specific needs. This article explores three main categories of backup solutions: tape drives, backup software, and cloud backup subscriptions, highlighting their features, advantages, and use cases.
The Importance of Backup Solutions
Backups provide a safety net for data by creating copies that can be restored during emergencies. The ideal backup solution should:
- Minimize data loss by enabling frequent backups.
- Ensure quick recovery to maintain business continuity.
- Offer scalability to handle growing data volumes.
- Provide security to protect backups from unauthorized access or corruption.
- Each backup method has its unique strengths, making it vital to understand their workings to select the most suitable solution.
Tape Drives: The Old-School Reliable Backup Option
Tape drives are one of the oldest data backup technologies, yet they remain relevant due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. They use magnetic tape to store data and are often employed for archival purposes in large enterprises.
Advantages of Tape Drives
- Cost-Effective for Large Data Sets: Per-terabyte costs are much lower than disk or cloud storage, making them ideal for long-term retention.
- Durability: Magnetic tapes have a lifespan of 20-30 years when stored properly.
- Portability: Tape cartridges are easy to transport, making them suitable for offsite storage.
Use Cases for Tape Drives
- Cold Storage: Ideal for data that is infrequently accessed but must be retained for compliance or historical purposes.
- Disaster Recovery: Tapes can be stored offsite, offering protection against localized disasters like fires or floods.
- Limitations of Tape Drives
- Slow Data Retrieval: Accessing data on tape is sequential, which makes it slower compared to disk or cloud storage.
- Physical Vulnerability: While durable, tapes can be damaged if not stored properly.
Backup Software: The Heart of Automated Backup Strategies
Backup software plays a crucial role in creating, managing, and restoring backups across different storage mediums. It provides the intelligence and automation needed for efficient data protection.
Key Features of Backup Software
- Automation: Schedules regular backups without manual intervention.
- Incremental Backups: Saves only the changes made since the last backup, reducing storage requirements.
- Data Compression and Encryption: Reduces backup size and secures data from unauthorized access.
- Support for Multiple Platforms: Many backup tools support servers, desktops, mobile devices, and virtual machines.
- Disaster Recovery Features: Some software includes tools for quick recovery or even bootable backups to minimize downtime.
Popular Backup Software Solutions
- Veeam Backup & Replication: Known for its advanced features, including real-time monitoring and support for virtual environments like VMware and Hyper-V.
- Acronis Cyber Protect: Combines backup with cybersecurity features to defend against ransomware.
- Commvault: Scalable for enterprise needs, offering comprehensive backup, recovery, and data management capabilities.
Advantages of Backup Software
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces make setup and management simple.
- Flexibility: Compatible with different storage mediums, including local disks, tape drives, and cloud services.
- Centralized Management: Allows administrators to monitor and control backups for multiple systems from a single console.
Cloud Backup Subscriptions: The Modern Backup Solution
Cloud backup solutions have revolutionized data protection by offering secure, scalable, and always-accessible backups. These services store data on remote servers managed by third-party providers.
How Cloud Backup Works
Data is encrypted and transmitted over the internet to a cloud provider’s data center. Backups can be scheduled to occur automatically, and incremental backups reduce bandwidth usage by only uploading changed data. Restores can be initiated from any location with an internet connection.
Advantages of Cloud Backups
- Scalability: Easily expand storage as data volumes grow without investing in hardware.
- Accessibility: Backups are accessible from anywhere, facilitating quick recovery in distributed environments.
- Managed Services: Providers handle maintenance, security, and updates, reducing administrative overhead.
Notable Cloud Backup Providers
- AWS Backup: A comprehensive service offering seamless backup integration with Amazon Web Services.
- Microsoft Azure Backup: Scales with business needs and provides robust data protection features.
- Backblaze: Affordable and user-friendly, suitable for small to medium-sized businesses.
Use Cases for Cloud Backups
- Business Continuity: Enables rapid recovery in the event of disasters or cyberattacks.
- Mobile Workforce: Ideal for organizations with remote or hybrid employees, ensuring data protection across distributed teams.
Challenges with Cloud Backup
- Dependence on Internet Connectivity: Restoring large data sets can be time-consuming with slow internet connections.
- Ongoing Costs: While hardware investments are avoided, recurring subscription costs may add up over time.
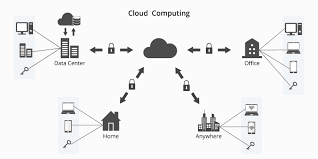
Choosing the Right Backup Solution
The best backup strategy often involves combining multiple solutions to address varying requirements. For instance:
- Small Businesses: May prefer cloud backups for simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
- Enterprises: Often use hybrid solutions combining tape drives for archiving, software for automation, and cloud for disaster recovery.
Key Factors to Consider
- Data Volume: Large data sets may benefit from the cost-efficiency of tape or hybrid solutions.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): If quick restores are essential, cloud or disk-based backups may be better suited.
- Budget: Tape drives offer a lower upfront cost for long-term storage, while cloud backups have predictable subscription costs.
- Compliance Requirements: Industries with strict data retention laws may require a mix of solutions to meet regulatory standards.
Best Practices for Effective Backups
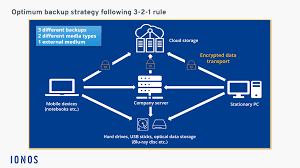
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Keep three copies of data, stored on two different media, with one copy offsite.
- Test Restorations Regularly: Periodically verify that backups can be restored successfully.
- Encrypt Backup Data: Ensure data is encrypted during transit and storage to protect against breaches.
- Use Versioning: Maintain multiple versions of files to protect against accidental changes or corruption.
- Monitor Backup Processes: Set up alerts for failed backups or low storage space to address issues proactively.
Conclusion
Backup solutions like tape drives, backup software, and cloud subscriptions cater to diverse needs, ensuring data is protected against a wide range of risks. Tape drives are an excellent choice for cost-effective archival storage, backup software offers automation and centralized management, and cloud backups provide unparalleled accessibility and scalability.
The key to an effective backup strategy lies in evaluating organizational needs and creating a hybrid approach that balances cost, speed, and reliability. With the right solutions in place, businesses can protect their critical data and ensure resilience against potential disruptions.










Leave a comment