Ensuring uninterrupted access to power is critical in both personal and professional settings. Power solutions safeguard sensitive electronic devices, enable mobility, and protect against damage caused by power fluctuations. This article explores Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS), Surge Protectors, and Power Banks & Charging Stations, discussing their importance, types, and applications.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)

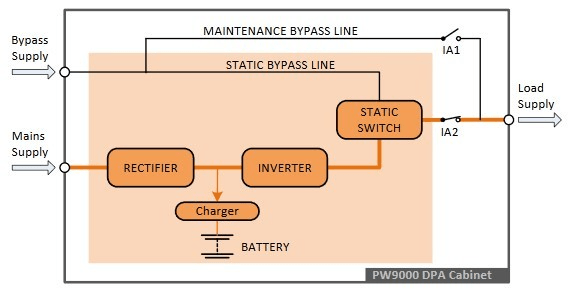
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a device that provides backup power and protects electronics from power fluctuations such as surges, brownouts, and outages. A UPS is essential for environments where power interruptions can lead to data loss, equipment damage, or operational downtime.
How a UPS Works
- Normal Operation: During regular power supply, the UPS charges its internal battery and monitors power quality.
- Power Failure: When a disruption occurs, the UPS instantly switches to battery power, ensuring a seamless transition without interrupting connected devices.
Types of UPS Systems
1. Standby UPS
Designed for basic protection, it switches to battery power when it detects a problem.
Ideal for home computers and small electronic devices.
Example: Basic models used for home offices or small setups.
2. Line-Interactive UPS
Contains voltage regulators that stabilize minor fluctuations without switching to battery power.
Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses.
Example: Protecting point-of-sale (POS) systems and networking equipment.
3. Online (Double-Conversion) UPS
Provides the highest level of protection by constantly converting incoming power into battery power and back.
Ideal for critical systems like data centers and medical equipment.
Example: Servers, healthcare equipment, and industrial machinery.
Advantages of a UPS
- Prevents data loss by providing sufficient time to save files and shut down systems properly.
- Protects sensitive equipment from voltage spikes and sags.
- Ensures continued operation of critical systems during short power outages.
Surge Protectors
A Surge Protector is a device designed to shield electronics from voltage spikes caused by power surges, which can result from lightning strikes, electrical faults, or sudden changes in power supply.
How Surge Protectors Work
Surge protectors divert excess voltage to the ground, ensuring that only a safe level of electricity reaches connected devices.
Types of Surge Protectors
1. Basic Surge Strips
- Multi-outlet strips with surge protection features.
- Commonly used for household appliances, TVs, and computers.
- Whole-House Surge Protectors
- Installed at the main electrical panel to protect an entire home or office.
- Suitable for areas prone to frequent electrical surges.
2. Data Line Surge Protectors
- Protects Ethernet, coaxial, and telephone lines in addition to power lines.
- Often used in networking and telecommunication setups.
Advantages of Surge Protectors
- Safeguards expensive electronics from damage.
- Prolongs the lifespan of devices by preventing overheating and stress during surges.
- Affordable and easy to install.
What to Look for in a Surge Protector
- Joule Rating: Higher ratings indicate better surge absorption capacity.
- Number of Outlets: Ensure enough outlets to accommodate all devices.
- Indicator Lights: Show the operational status of the surge protection mechanism.

Power Banks & Charging Stations
Power banks and charging stations are portable power solutions that keep devices charged on the go or in shared environments. They are indispensable in today’s mobile-dependent world.
Power Banks
A power bank is a compact battery pack that can recharge smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other portable electronics.
Key Features of Power Banks
- Capacity: Measured in milliampere-hours (mAh).
- 5,000–10,000 mAh: Ideal for smartphones and small gadgets.
- 20,000+ mAh: Suitable for laptops and multiple device charging.
- Output Ports: USB-A, USB-C, and wireless charging options.
- Fast Charging: Features like Quick Charge (QC) or Power Delivery (PD) for faster charging speeds.
- Portability: Lightweight and compact designs for easy transport.
Advantages of Power Banks
- Provides emergency power in remote or outdoor locations.
- Keeps devices operational during travel or power outages.
- Supports multiple recharges depending on capacity.

Charging Stations
Charging stations are centralized hubs with multiple ports for charging several devices simultaneously.
Applications of Charging Stations
- Workplaces: Keeps employees’ devices charged in collaborative environments.
- Homes: Ideal for families with multiple smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches.
- Public Spaces: Found in airports, libraries, and hotels for public use.
- Features to Look for in Charging Stations
- Power Output: Ensure sufficient power to charge multiple devices efficiently.
- Port Types: USB-A, USB-C, and wireless pads for compatibility with a wide range of devices.
- Smart Charging: Balances power distribution to optimize charging speed for each device.
- Design: Compact designs with cable management features to reduce clutter.
Advantages of Charging Stations
- Reduces clutter by consolidating power needs into a single device.
- Offers convenience in environments with multiple users or devices.
- Supports fast charging and prevents overloading of traditional power outlets.

Comparison of Power Solutions
| Feature | UPS | Surge Protector | Power Banks & Charging Stations |
| Primary Function | Backup power and protection | Protection from power surges | Portable or centralized charging |
| Best Use Cases | Critical systems and servers | Home appliances and computers | Mobile devices and shared spaces |
| Cost Range | Moderate to High | Low | Low to Moderate |
| Lifespan | 3–5 years (batteries) | 3–5 years | 2–4 years (battery capacity) |
Best Practices for Power Solutions
- Assess Power Needs: Determine the criticality of devices to prioritize power solution investments.
- Combine Solutions: Use a surge protector with a UPS for enhanced protection.
- Regular Maintenance: Test UPS batteries periodically and replace them when necessary.
- Choose Reliable Brands: Opt for trusted manufacturers with safety certifications.
- Stay Updated: Keep power banks and charging stations compatible with the latest devices by choosing those with updated port types and features.
Conclusion
Power solutions such as Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS), Surge Protectors, and Power Banks & Charging Stations are crucial for protecting electronics, ensuring seamless operations, and enabling mobility. Whether safeguarding a data center, maintaining continuity during a power outage, or charging devices on the go, these tools provide essential support for modern lifestyles and business environments.
Investing in high-quality power solutions tailored to specific needs not only protects valuable equipment but also enhances productivity and peace of mind.









Leave a comment